
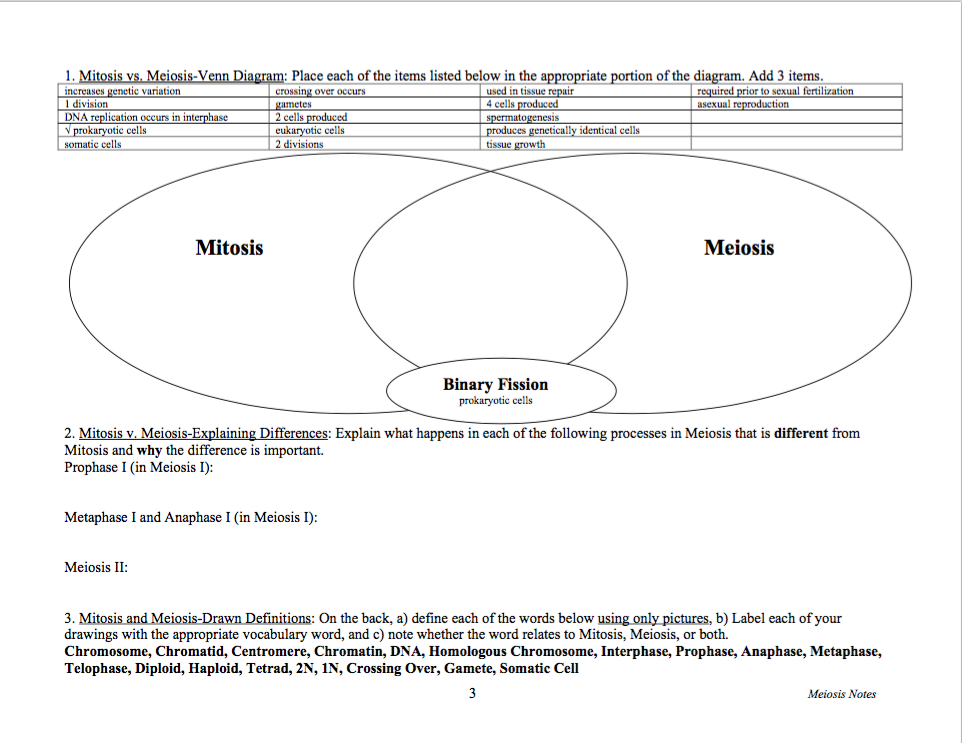
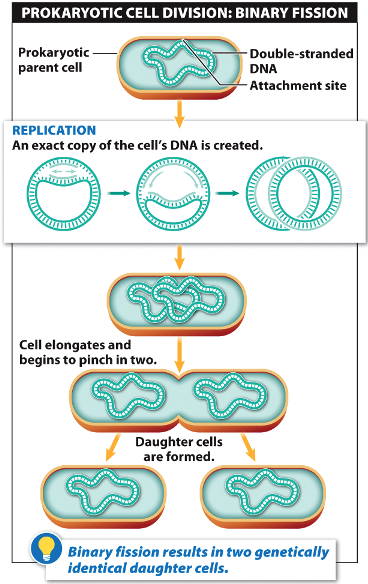
Step one: the circular DNA and plasmid (s) replicate. Give a brief definition for binary fission. They cell makes copies of its genetic material, before splitting into two daughter cells. This helps spore producing bacteria to survive long enough for spore production. Binary fission is when prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria, replicate by a type of simple cell division. the area on the chromosome (specific sequence) where replication starts. As dying cells lyse or break open, they spill their contents into the environment making these nutrients available to other bacteria. a structure that contains most of the organisms DNA. In the death phase, the number of living cells decreases exponentially and population growth experiences a sharp decline. a tumor that is cancerous and can spread. Binary Fission A type of asexual reproduction in which the parent cell divides into two genetically identical daughter cells. A mass of abnormal cells that remains at the site of its origin. disease in which abnormal cells divide uncontrollably. Death Phase: As nutrients become less available and waste products increase, the number of dying cells continues to rise. the division of a prokaryotic cell into two offspring cells.Spore forming bacteria produce endospores in this phase and pathogenic bacteria begin to generate substances (virulence factors) that help them survive harsh conditions and consequently cause disease. Under the less favorable conditions, competition for nutrients increases and the cells become less metabolically active. This results in no overall population growth. The term protist typically is used in reference to a eukaryote that is not a true animal, plant, or fungus or in reference to a eukaryote that lacks a multicellular stage. They may share certain morphological and physiological characteristics with animals or plants or both. Bacterial cell growth reaches a plateau, or stationary phase, where the number of dividing cells equal the number of dying cells. protist, any member of a group of diverse eukaryotic, predominantly unicellular microscopic organisms. Stationary Phase: Eventually, the population growth experienced in the log phase begins to decline as the available nutrients become depleted and waste products start to accumulate.DNA replicates and transfers from one cell to the other 3. A cytoplasmic bridge forms between two cells 2. It is in this growth phase that antibiotics and disinfectants are most effective as these substances typically target bacteria cell walls or the protein synthesis processes of DNA transcription and RNA translation. a type of asexual reproduction in which one bacterial cell divides, creating two identical offspring define horizontal gene transfer transfer of genes between cells of the same generation define conjugation 1. Metabolic activity is high as DNA, RNA, cell wall components, and other substances necessary for growth are generated for division.
This is the time when the cells are dividing by binary fission and doubling in numbers after each generation time. Exponential (Log) Phase: After the lag phase, bacterial cells enter the exponential or log phase.These cells increase in size, but no cell division occurs in the phase.
A small group of cells are placed in a nutrient rich medium that allows them to synthesize proteins and other molecules necessary for replication.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
